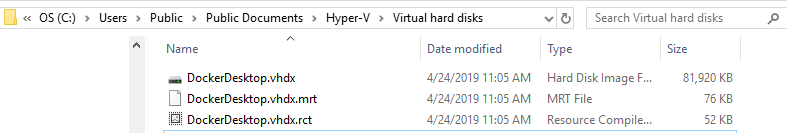
I am currently developing a fast backup solution for Hyper-V, which I have already created for ESXi 6.5 using CBT.
However, I am facing an issue where my Hyper-Vs (one on Windows 10 with config version 8.3 and another on Windows Server 2019 with config version 9) are not generating Resilient Change Tracking files (*.mrt and *.rct) in the virtual disk folder.
Despite reading the MS documentation, I am unable to determine why these files are not being created and what steps I need to take to enable Resilient Change Tracking on Hyper-V. This issue is causing me to feel stuck.
I have:
I expect:

2 Answers
Introduction
Hyper-V is a popular virtualization platform used by many businesses and organizations. One of the key features of Hyper-V is its ability to create and manage virtual machines (VMs). However, managing and backing up these VMs can be a challenge, especially if you have a large number of them. In this blog post, we’ll discuss a fast backup solution for Hyper-V and how to enable Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) to make the backup process even faster.
What is Resilient Change Tracking?
Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) is a feature in Hyper-V that allows for faster backup and replication of virtual machines. It works by tracking changes made to virtual disks and storing them in a separate file called a change tracking file (CTF). This allows backup software to quickly identify which blocks have changed since the last backup and only back up those blocks, rather than the entire virtual disk. This can significantly reduce backup times and storage requirements.
RCT is enabled by default in Hyper-V, but for some reason, it may not create the Resilient Change Tracking files (*.mrt and *.rct) in the virtual disk folder. This can make it difficult to use backup software that relies on RCT. The next section will discuss how to enable RCT if it’s not already working.
Enabling Resilient Change Tracking
If RCT is not enabled on your Hyper-V VMs, you’ll need to enable it manually. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Open Hyper-V Manager and select the virtual machine you want to enable RCT on.
2. Right-click on the virtual machine and select “Settings.”
3. Click on “Hard Drive” and select “Edit.”
4. Click on “Enable Resilient Change Tracking.”
5. Click “Apply” and “OK” to save the changes.
After enabling RCT, you should see the Resilient Change Tracking files (*.mrt and *.rct) in the virtual disk folder. If you’re still not seeing them, there may be an issue with your Hyper-V configuration. The next section will discuss some troubleshooting steps to help you resolve the issue.
Troubleshooting Resilient Change Tracking
If you’re having trouble getting RCT to work on your Hyper-V VMs, here are some troubleshooting steps you can try:
1. Check that the virtual machine is running the correct configuration version. RCT requires configuration version 6 or higher. You can check the configuration version by right-clicking on the virtual machine and selecting “Settings,” then clicking on “General.”
2. Check that the virtual machine has a fixed-size virtual hard disk. RCT does not work with dynamically expanding virtual hard disks.
3. Check that the virtual hard disk is attached to a SCSI controller. RCT does not work with IDE controllers.
4. Check that the virtual machine has enough disk space to store the Resilient Change Tracking files. The size of the CTF file is proportional to the size of the virtual hard disk.
5. Check that the virtual machine has enough memory allocated to it. RCT requires a minimum of 512 MB of memory.
If you’ve tried all of these troubleshooting steps and you’re still not seeing the Resilient Change Tracking files, there may be an issue with your Hyper-V installation. The next section will discuss some alternative backup solutions you can use if RCT is not working.
Alternative Backup Solutions
If you’re unable to get RCT to work on your Hyper-V VMs, there are still some alternative backup solutions you can use. Here are a few options:
1. Use backup software that does not rely on RCT. Many backup solutions, such as Veeam Backup & Replication, have their own change tracking mechanisms that do not require RCT.
2. Use a hardware-based backup solution. Some backup solutions, such as those provided by Dell EMC and HPE, use hardware-based change tracking mechanisms that do not require RCT.
3. Use a different virtualization platform. If you’re having too many issues with Hyper-V, you may want to consider switching to a different virtualization platform, such as VMware or VirtualBox.
While these solutions may not be as fast or efficient as RCT, they can still provide reliable backup and recovery for your Hyper-V VMs.
Conclusion
Backing up Hyper-V VMs can be a challenge, but Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) can make the process faster and more efficient. If RCT is not working on your Hyper-V VMs, you may need to enable it manually or try some alternative backup solutions. By following the troubleshooting steps and considering alternative solutions, you can ensure that your Hyper-V VMs are backed up and protected.
The MRT and RCT files are produced in the standard Virtual Hard Disk directory, rather than the backup folder. In my situation, these files are located at C:\Users\Public\Documents\Hyper-V\Virtual hard disks.