I currently have a dual boot setup on my computer with Windows 7 and Ubuntu 18.04 installed on separate partitions. In the past, I have replaced Linux distributions by formatting the partition and installing a new one, but I’m wondering if I can do the same thing with Windows 10.
I’ve heard about Grub errors that can occur when removing a Linux distribution from a dual boot setup. If I replace Ubuntu with Windows 10, could I encounter these errors?
Ideally, I’d like to avoid dealing with Grub and the bootloader on my computer, as I don’t want to risk losing the Windows 7 partition. However, I’m not worried about losing anything on the Ubuntu partition as I know it will be formatted.
3 Answers
Introduction
If you’re looking to dual boot Windows 7 and Windows 10 by replacing Ubuntu, you’re in luck! It’s definitely possible to replace Ubuntu with Windows 10 without any major issues. However, you’ll need to take a few precautions to avoid any potential problems.
In this blog post, we’ll go over the steps you’ll need to take to replace Ubuntu with Windows 10, including how to avoid any Grub errors that may occur. We’ll also discuss some of the benefits of dual booting Windows 7 and Windows 10, as well as some potential drawbacks.
Benefits of Dual Booting Windows 7 and Windows 10
There are several benefits to dual booting Windows 7 and Windows 10. First and foremost, it allows you to take advantage of the features and benefits of both operating systems. For example, if you have programs or applications that only run on Windows 7, you can still use them while also having access to newer programs and applications that are only available on Windows 10.
Additionally, dual booting can be a great way to test out new software or operating systems without having to fully commit to them. You can try out Windows 10 and all of its features while still having the option to boot into Windows 7 if you encounter any issues or problems.
Steps to Replace Ubuntu with Windows 10
Now, let’s get into the steps you’ll need to take to replace Ubuntu with Windows 10. Here’s what you’ll need to do:
1. First, you’ll need to create a bootable Windows 10 USB drive or DVD. You can do this by downloading the Windows 10 Media Creation Tool from Microsoft’s website and following the instructions provided.
2. Once you have your bootable Windows 10 USB drive or DVD, you’ll need to boot your computer from it. You can do this by changing the boot order in your BIOS settings. Make sure to save your changes before exiting the BIOS.
3. Next, you’ll need to select the “Custom” installation option when prompted. This will allow you to choose which partition to install Windows 10 on.
4. You’ll then be prompted to select a partition to install Windows 10 on. Make sure to select the partition that currently has Ubuntu installed on it. You can identify the partition by its size and file system type (it should be formatted as ext4).
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process. Once the installation is complete, your computer should automatically boot into Windows 10.
Avoiding Grub Errors
As mentioned earlier, there is a risk of encountering Grub errors when removing a Linux distribution from a dual boot setup. However, you can avoid these errors by following the steps outlined above. By selecting the “Custom” installation option and choosing the correct partition to install Windows 10 on, you’ll effectively remove Ubuntu from your computer without encountering any Grub errors.
Potential Drawbacks of Dual Booting
While there are many benefits to dual booting Windows 7 and Windows 10, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider. For example, dual booting can take up a significant amount of space on your hard drive. You’ll need to make sure you have enough space to accommodate both operating systems, as well as any programs and applications you plan to install.
Additionally, dual booting can be a bit more complicated than running just one operating system. You’ll need to be comfortable with changing BIOS settings and partitioning your hard drive, as well as troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Conclusion
Dual booting Windows 7 and Windows 10 can be a great way to take advantage of the benefits of both operating systems. By replacing Ubuntu with Windows 10, you can enjoy all of the features and programs of Windows 10 while still having the option to boot into Windows 7 if needed.
Just remember to take the necessary precautions to avoid any potential Grub errors, and be aware of the potential drawbacks of dual booting. With a bit of preparation and know-how, you can successfully dual boot Windows 7 and Windows 10 and enjoy the best of both worlds.
Yes, it is possible to dual boot Windows 7 and Windows 10 by replacing Ubuntu. However, you will need to be careful and follow a specific process to ensure that the dual boot is set up correctly and that you do not lose access to either of the two operating systems.
Here is the general process you can follow:
- Back up all of your important data and documents. This is important because you will be formatting the Ubuntu partition, which will erase all of the data on it.
- Boot from a Windows 10 installation media, such as a USB drive or DVD. You can create a bootable Windows 10 installation media using the Windows Media Creation Tool, which you can download from Microsoft’s website.
- When prompted, select the custom installation option and choose the Ubuntu partition as the destination for the installation. Make sure you select the correct partition, as formatting the wrong partition could cause serious problems.
- Follow the prompts to complete the installation of Windows 10. During the installation process, the Windows 10 installer will overwrite the Grub bootloader with its own bootloader, which will allow you to boot into either Windows 7 or Windows 10.
- After the installation is complete, you should be able to boot into either Windows 7 or Windows 10 by selecting the appropriate option from the boot menu.
It is important to note that removing Ubuntu and replacing it with Windows 10 will overwrite the Grub bootloader, which may cause issues with booting into Windows 7 if the process is not done correctly. Therefore, it is important to follow the steps carefully and to make sure you have a backup of all of your important data before you begin.
Before proceeding, it is important to confirm the type of disk installed as EFI BIOS necessitates a GPT disk. To do so, navigate to Disk Management and right-click on the “Disk 0” label in the lower pane. From there, select “Properties,” and the “Partition style” entry can be found in the “Volumes” tab.
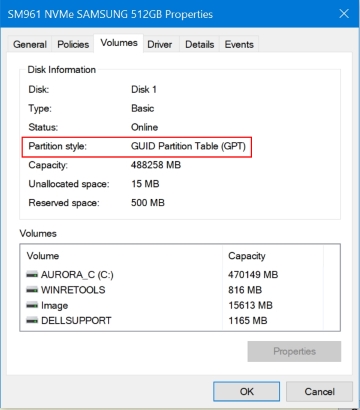
The solution for EFI/GPT involves the EFI BIOS managing the boot process by utilizing files found in the EFI partition. The approach presented here is derived from a response provided in the post:
Uninstall Grub and use Windows bootloader:
- Run a
cmd.exeprocess with administrator privileges- Run
diskpart- Type:
list diskthensel disk Xwhere X is the drive your boot files reside on- Type
list volto see all partitions (volumes) on the disk (the EFI volume will be formatted in FAT, others will be NTFS)- Select the EFI volume by typing:
sel vol Ywhere Y is theSYSTEMvolume (this is almost always the EFI partition)- For convenience, assign a drive letter by typing:
assign letter=Z:where Z is a free (unused) drive letter- Type
exitto leave disk part- While still in the
cmdprompt, type:Z:and hit enter, where Z was the drive letter you just created.- Type
dirto list directories on this mounted EFI partition- If you are in the right place, you should see a directory called
EFI- Type
cd EFIand thendirto list the child directories insideEFI- Type
rmdir /S ubuntuto delete the ubuntu boot directoryAssuming you only ever had two operating systems (Win 10 & Ubuntu) you
should now be able to boot directly to Windows without hitting the
black grub screen.
It is now possible to proceed with the installation of Windows 10, ensuring that the correct partition is selected (the default may suggest an upgrade to the Windows 7 partition). However, it is crucial to recognize the potential severity of this process, as a mistake could result in permanent damage to the disk. As a precautionary measure, it is recommended to create a backup image of the entire disk before beginning. AOMEI Backupper Freeware is a personal favorite tool for this purpose.
The solution for BIOS/MBR involves having a Windows 7 installation disk on hand. Once you’ve booted from it, select the Repair option. The system will automatically scan for startup issues, and from there, select the Command Prompt option and input the subsequent commands:
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
Enter exit to close the Command Prompt and restart your computer.